Sustainable Coffee Farming Practices: From Seed to Harvest

Affiliate Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. This post may also contain other affiliate links, meaning I may earn a small commission if you buy through them, at no extra cost to you. Your support helps keep this site running and allows me to continue sharing great content. Thank you!
Coffee is not just a beverage; it’s a global industry and an essential part of daily life for millions. However, as the demand for coffee continues to grow, the way coffee is produced must evolve to meet not only economic needs but also environmental and social responsibilities. Sustainable coffee farming practices have emerged as a solution, transforming traditional methods into eco-friendly approaches that ensure both high-quality coffee and a healthier planet.
The journey from seed to cup is a complex process that requires careful attention to every step. From planting to harvesting and beyond, sustainable practices such as organic farming, shade-grown coffee, and fair trade certifications are now shaping the future of coffee farming. These methods are designed not only to protect the environment but also to support local communities and help farmers cope with challenges like climate change and rising production costs.
Adopting sustainable farming practices benefits more than just the coffee plants. Techniques like water conservation, composting to maintain soil health, and pest management through natural means are critical in ensuring that coffee farming can thrive even in an unpredictable climate. By maintaining soil fertility and using water resources efficiently, farmers are able to create more resilient ecosystems that support the long-term viability of coffee production.
Shade-grown coffee, for instance, is not only an eco-friendly approach but also a method that enhances the quality of the beans. By growing coffee under a canopy of trees, farmers can protect the soil from erosion, reduce the need for chemical fertilizers, and provide habitats for local wildlife. This approach creates a balanced ecosystem, which ultimately results in better coffee beans and a healthier environment.
Sustainable coffee farming also plays a significant role in promoting biodiversity. By integrating methods like shade-growing and organic farming, farmers can preserve local ecosystems and reduce the environmental impact of coffee production. Fair trade practices further ensure that farmers receive fair compensation for their work, contributing to the economic sustainability of farming communities.
In the following sections, we’ll explore the journey of sustainable coffee farming in greater detail—from the historical origins of coffee farming to the innovative techniques being used today. Whether you’re a coffee enthusiast or simply curious about the future of coffee production, this guide will show how sustainable practices are shaping the entire coffee production process.
To truly understand sustainable coffee farming today, we must first explore its roots. Let’s look back at the origins of coffee farming and how early practices laid the groundwork for the eco-friendly techniques now in use.
The Origins of Coffee Farming
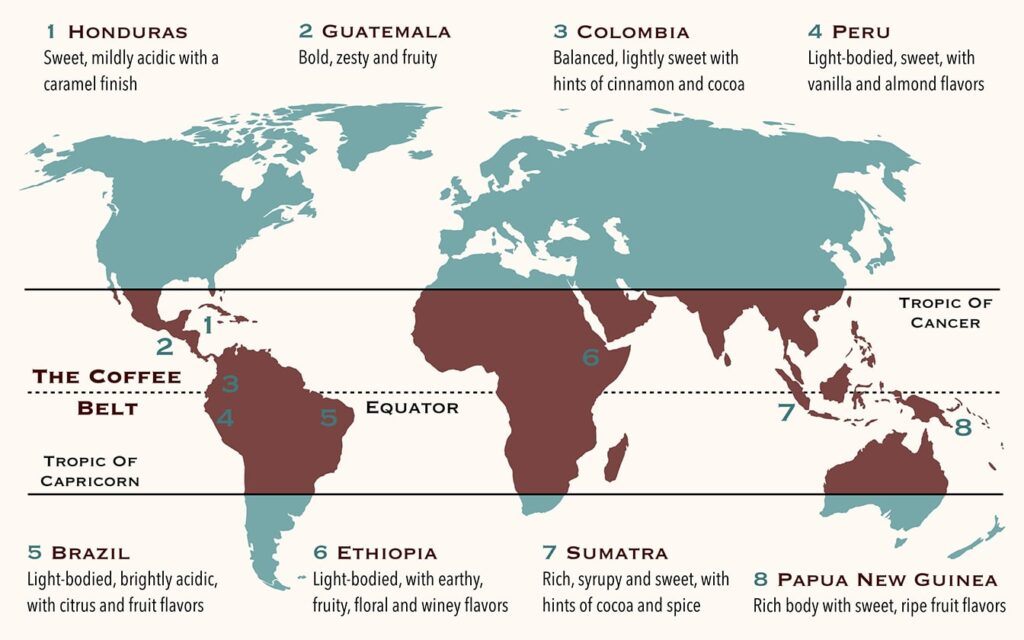
Coffee’s story is as rich and layered as the beverage itself. The origins of coffee farming trace back to the highlands of Ethiopia, where legend has it that a goat herder named Kaldi first discovered the energizing effects of coffee beans. From these humble beginnings, coffee made its way to the Arabian Peninsula, where it became a central part of culture and trade.
As coffee spread across the globe, it found its ideal growing conditions in the tropics. Coffeehouses began popping up in Europe by the 17th century, becoming hubs of social and intellectual activity. Soon after, European colonists introduced coffee plants to tropical regions, giving birth to the Coffee Belt—the regions around the equator where coffee is grown today.
Each region within the Coffee Belt brings its own unique flavors to the global coffee market:
- Central America: Known for its bright, clean flavor profiles.
- Africa: Often characterized by fruity or floral notes.
- Asia: Produces coffee with earthy or spicy undertones.
Historically, traditional coffee farming methods were not always sustainable. As coffee production expanded, practices like deforestation and the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides led to environmental degradation. However, increasing awareness of environmental issues has transformed coffee farming.
Today, many farms are adopting sustainable coffee farming practices, including:
- Shade-grown coffee to protect ecosystems and enhance flavor.
- Organic farming reduces the need for chemical inputs.
- Fair trade certifications ensure that farmers are paid fairly and work in ethical conditions.
With an understanding of coffee’s origins, the next step is examining how different plant varieties and their unique farming requirements contribute to sustainable coffee production.
Coffee Plant Varieties and Their Farming Requirements
When it comes to coffee, variety is the spice of life. The diversity of coffee plant varieties around the world creates a rich spectrum of flavors, each suited to different growing conditions and farming techniques. Understanding these varieties is essential for sustainable coffee farming, as each has specific requirements that affect how it’s cultivated.
There are four main coffee varieties grown globally:
- Arabica: This is the most popular variety, accounting for about 60% of the world’s coffee production. Arabica beans are known for their smooth, mild flavor and higher acidity. They thrive in high-altitude regions with mild temperatures and plenty of moisture. However, Arabica plants are sensitive to pests and diseases, which makes sustainable practices like shade-growing and organic farming vital for maintaining healthy crops.
- Robusta: Known for its strong, bitter flavor, Robusta is a hardier plant compared to Arabica. It can tolerate higher temperatures and lower altitudes, making it easier to cultivate in harsher conditions. Although more resilient, Robusta benefits from sustainable methods like intercropping and organic fertilizers, which help protect the environment and improve soil health.
- Liberica: Less common than Arabica and Robusta, Liberica beans have a distinct, sometimes smoky flavor. These plants are resilient and can grow in areas where other coffee varieties might struggle, making them suitable for regions with challenging growing conditions.
- Excelsa: Often considered a sub-variety of Liberica, Excelsa adds complexity to coffee blends with its tart, fruity notes. Though rare, it contributes a unique flavor profile that enhances specialty coffee products. Like Liberica, Excelsa plants benefit from biodiversity-friendly farming practices, which help preserve their distinct characteristics and support local ecosystems.
Farming Requirements
The cultivation of these varieties depends on specific environmental factors, including altitude, climate, and soil conditions. Here’s a breakdown of the primary farming requirements:
| Coffee Variety | Altitude | Temperature | Rainfall |
| Arabica | 600–2,000 meters | 15–24°C (59–75°F) | 1,500–2,000 mm annually |
| Robusta | Sea level to 600 meters | 24–30°C (75–86°F) | 1,500–2,000 mm annually |
| Liberica | Varies, often lower altitudes | Varies by region | Can tolerate tougher conditions |
| Excelsa | Similar to Liberica | Similar to Liberica | Similar to Liberica |
This table simplifies the key requirements for growing each variety, making it easy to compare their needs.
Sustainable Farming Practices:
Regardless of the variety, sustainable farming practices are crucial for maintaining soil fertility and minimizing environmental impact. Some effective techniques include:
- Shade-grown coffee: Growing coffee under the natural canopy of trees replicates the plant’s natural environment, preserving biodiversity and improving bean quality.
- Organic farming: Avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides protects soil health and reduces environmental pollution. Composting and using green manures are common practices that keep the soil rich and fertile.
- Intercropping: Planting coffee alongside other crops helps manage pests naturally, improves soil health, and reduces the need for chemical inputs.
By focusing on sustainable practices tailored to each coffee variety’s needs, farmers can increase productivity while protecting the environment and producing high-quality beans.
Now that we understand the different coffee plant varieties, let’s move on to the sustainable methods farmers use to plant and grow healthy coffee crops while protecting the environment.
Planting and Growing Coffee: A Sustainable Approach
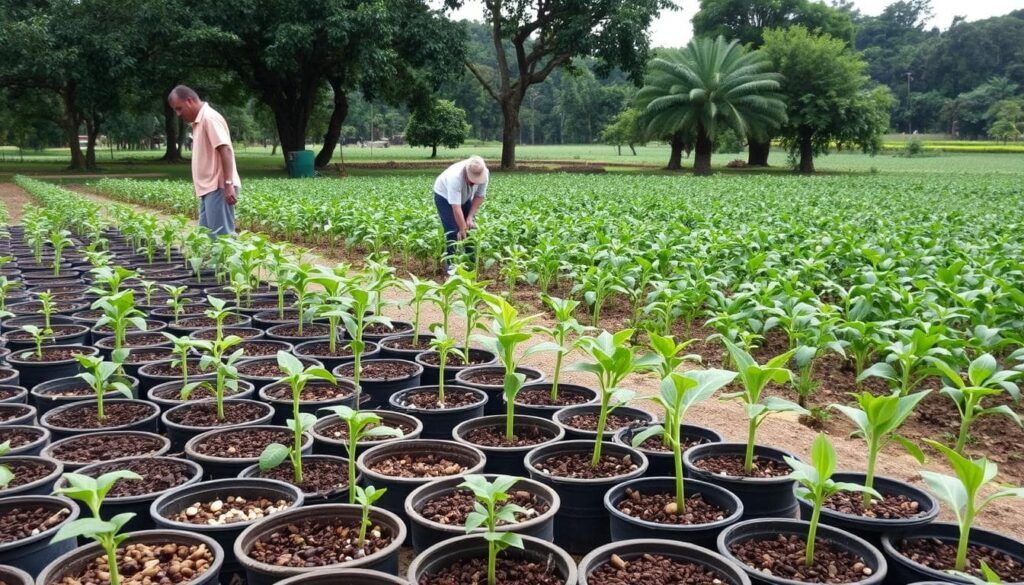

The journey of coffee begins with the planting of seeds, but growing coffee sustainably requires careful planning and attention to detail at every stage of the process. From selecting disease-resistant seeds to employing eco-friendly farming methods, sustainable practices ensure that coffee plants grow healthy while protecting the environment.
Choosing the Right Seeds:
Sustainable coffee farming starts with selecting high-quality, disease-resistant seeds. These seeds form the foundation for a productive and resilient crop. Once sprouted, seedlings are often grown in nurseries for up to a year, where they receive the nutrients and care needed to develop strong root systems.
The Role of Shade-Grown Coffee:
One of the most effective sustainable farming methods is shade-grown coffee. Coffee naturally grows best under the shade of trees, replicating its natural environment in tropical forests. By adopting this method, farmers can:
- Protect local flora and fauna, as trees provide habitats for wildlife.
- Reduce soil erosion and preserve soil fertility through natural compost from falling leaves.
- Minimize the need for chemical fertilizers, as the enriched soil structure retains nutrients and moisture more effectively.
Shade-grown coffee is an eco-friendly approach that promotes biodiversity while improving the overall quality of the coffee beans.
Maintaining Soil Health:
Healthy soil is the backbone of sustainable farming. Several organic practices are used to maintain soil fertility and increase productivity:
- Composting: By using organic matter like coffee pulp and leaves, farmers enrich the soil with nutrients, boosting plant health and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Mulching: Covering the soil with mulch helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and maintain a consistent temperature around the roots.
- Crop rotation: Alternating between different crops helps prevent soil depletion, allowing for sustained coffee production over the years.
Water Conservation:
Water is a vital resource in coffee farming, and sustainable methods focus on reducing water waste while keeping crops healthy. Techniques such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting help conserve water, ensuring that farms can thrive even in regions prone to drought.
Pest Management:
Sustainable pest control methods minimize the use of harmful chemicals. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies involve using natural predators, such as birds and beneficial insects, to control pests. Farmers may also plant specific crops alongside coffee that act as natural repellents, further reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Once coffee plants have flourished under these sustainable methods, it’s time to move to the next critical phase—harvesting. Here, farmers blend traditional hand-picking with modern techniques to ensure the highest-quality beans.
Harvesting Coffee Beans: Traditional Methods vs. Modern Innovations
After planting and growing, the next step is harvesting the coffee beans. This process is critical, as it impacts the final quality of the beans. Farmers gather the cherries using both traditional hand-picking methods and modern mechanical harvesting.
Traditional Hand-Picking Methods
In regions focused on high-quality Arabica beans, hand-picking is preferred. This method allows farmers to select only the ripest cherries, improving overall bean quality. However, this labor-intensive process requires significant time and effort, making it less sustainable for large-scale operations.
Modern Mechanical Harvesting
Larger farms, particularly those growing Robusta beans, often rely on mechanical harvesters. These machines quickly shake the cherries loose from the branches, reducing labor costs and speeding up the process. However, mechanical harvesting can sometimes result in mixed batches of ripe and unripe cherries, affecting quality.
Sustainable Harvesting Practices
To improve sustainability, many farmers are adjusting harvest times to account for climate patterns and experimenting with selective mechanical harvesters that minimize waste.
Summary of Harvesting Methods:
Traditional Hand-Picking
- Labor-intensive but ensures quality: Workers manually pick ripe cherries, producing a uniform batch of beans.
- Selective picking: Only ripe cherries are harvested, improving flavor and quality.
- Common on small farms: This method supports local employment and maintains high standards for specialty coffee.
- Costly due to labor demands: Hand-picking can be expensive, particularly for farms facing labor shortages.
Mechanical Harvesting
- Faster and cost-effective: Machines reduce the time and costs of harvesting, ideal for large plantations.
- Better for flat terrain: Suited for larger, flatter farms, where manual labor is impractical.
- Challenges with cherry selection: Machines may pick unripe cherries, affecting quality.
- Technological improvements: Selective harvesters help increase precision.

With the cherries harvested, the next crucial step is processing. This phase transforms the cherries into the beans we brew, and sustainable methods play a pivotal role in reducing environmental impact.
Processing Coffee Cherries: Sustainable Methods and Technology
Once coffee cherries are harvested, the journey of coffee beans is far from over. The processing stage transforms these cherries into the beans we know and love. Different processing methods not only influence the flavor of the coffee but also significantly impact the environment.
Sustainable processing methods aim to reduce water usage, minimize waste, and lower the carbon footprint of coffee production. To explore this fascinating process further, read my guide on coffee beans.
Wet, Dry, and Honey Processing Methods
There are three primary methods of processing coffee cherries: wet, dry, and honey processing. Each has its own advantages and environmental challenges.
- Wet Processing (Washed): This method removes the cherry pulp before the beans are fermented and washed. Wet processing can produce clean, bright flavors but is water-intensive. To mitigate environmental impact, many farms are adopting water-efficient systems that recycle and purify water during the process.
- Dry Processing (Natural): In this method, cherries are laid out in the sun to dry with the pulp still attached. It is the oldest and most eco-friendly process since it requires minimal water, but it can be time-consuming and susceptible to weather conditions. Drying beds, which improve airflow, are increasingly used to enhance sustainability and prevent mold.
- Honey Processing: This method is a hybrid of wet and dry processing. Some of the cherry’s mucilage is left on the beans during drying, resulting in a sweeter, fuller flavor. It uses less water than wet processing and is gaining popularity as a sustainable alternative.
Another key element in processing coffee sustainably is understanding the environmental impact of each method. The following table outlines the water usage, processing time, environmental impact, and flavor profile for the three main methods of coffee processing:
Table: Coffee Processing Methods and Their Environmental Impact
| Processing Method | Water Usage | Time | Environmental Impact | Flavor Profile |
| Wet Processing | High | Faster, with fermentation | Water-intensive but clean | Clean, bright flavors |
| Dry Processing | Low | Slower, weather-dependent | Minimal water usage | Bolder, fruitier flavors |
| Honey Processing | Moderate | Varies based on mucilage | Less water than wet process | Sweeter, fuller flavors |
As the coffee industry strives for sustainability, new technologies are reshaping traditional processing methods. Let’s explore some of the innovative techniques for making coffee processing more eco-friendly.
Innovations in Sustainable Processing
As sustainability becomes a growing focus within the coffee industry, new technologies are being introduced to make coffee processing more eco-friendly.
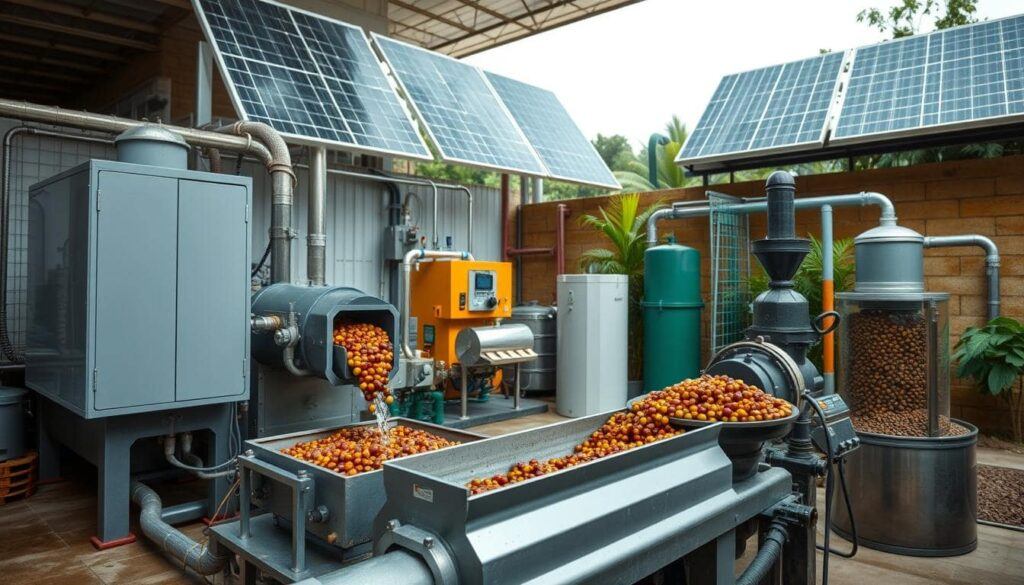

Here are some of the key innovations that are shaping the future of sustainable coffee processing:
- Eco-Pulpers and Demucilagers: These machines reduce the amount of water used in wet processing by mechanically removing the pulp and mucilage from the beans. This innovation helps conserve water while speeding up the processing time, making it both eco-friendly and efficient.
- Renewable Energy: Many coffee farms are now turning to renewable energy sources, such as solar power and biogas, to power their processing facilities. This reduces their reliance on fossil fuels and lowers their overall carbon footprint.
- Anaerobic Fermentation: This experimental processing method is being used to create unique flavor profiles by fermenting coffee beans without oxygen. Not only does this produce distinctive taste notes, but it also helps reduce the environmental impact of traditional fermentation processes.
- Carbonic Maceration: Inspired by winemaking techniques, carbonic maceration is being introduced in coffee processing to control fermentation and enhance flavor. This method is gaining popularity as a way to add value while maintaining sustainability.
These innovations represent the ongoing commitment of the coffee industry to reduce environmental impact while improving the quality and efficiency of coffee production.
With the beans processed, let’s look at how sustainable farming practices continue to play a crucial role in addressing challenges faced by coffee farmers around the world.
Sustainable Coffee Farming Practices
Sustainable coffee farming encompasses methods that protect the environment while supporting the communities involved in coffee production. These practices include shade-grown coffee, organic farming, and fair trade certifications.
Shade-Grown Coffee
Shade-grown coffee is one of the most effective sustainable methods, where coffee plants are cultivated under a natural tree canopy. This farming approach:
- Promotes biodiversity, providing habitats for various species of wildlife.
- Prevents soil erosion and helps retain moisture, improving soil fertility.
- Reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides by fostering a balanced ecosystem.
Organic Farming
Organic farming eliminates the use of synthetic chemicals, focusing on natural alternatives to improve soil health and crop resilience. Key organic practices include:
- Composting: Organic matter, such as coffee pulp, is used to enrich the soil with nutrients, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Natural Pest Control: Instead of pesticides, farms rely on natural methods like companion planting to protect crops.
Fair Trade Certifications
Fair trade ensures that farmers receive fair compensation for their work while promoting ethical labor conditions. By supporting fair trade practices, coffee buyers contribute to a more sustainable and equitable system, ensuring long-term viability for coffee-growing communities.
While sustainable practices have made strides in coffee farming, numerous challenges remain. From climate change to economic pressures, let’s examine how farmers are adapting to ensure the industry’s future.
Challenges in Coffee Farming
Coffee farming, while a source of livelihood for millions, faces a host of challenges that threaten the future of the industry. From the impacts of climate change to economic difficulties and labor shortages, coffee farmers must navigate complex issues to keep their farms sustainable. Understanding these challenges is crucial for supporting coffee farming communities and ensuring a steady supply of coffee.
Climate Change
Climate change poses one of the biggest threats to coffee farming. Rising temperatures, unpredictable weather patterns, and longer droughts are making it harder for coffee plants to thrive in traditional growing regions.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Coffee, particularly Arabica, requires a specific temperature range to grow properly. Warmer climates can reduce yields and lower the quality of the beans, forcing farmers to move to higher altitudes or experiment with hardier varieties.
- Rainfall Variability: Coffee plants are highly dependent on consistent rainfall. Longer droughts or unpredictable rainfall patterns can lead to water stress, affecting plant health and bean quality.
Economic Challenges
In addition to climate issues, economic challenges such as fluctuating coffee prices and rising production costs have made it increasingly difficult for smallholder farmers to earn a living. Global market volatility and a lack of access to credit can leave farmers vulnerable to financial hardship.
- Low Coffee Prices: When global coffee prices fall, farmers often struggle to cover the costs of production. This can lead to lower-quality beans or, in extreme cases, abandoning coffee farming altogether.
- High Production Costs: Sustainable farming practices, while beneficial in the long run, often require significant upfront investment. Organic fertilizers, renewable energy sources, and water-saving technology can be costly for small farms, making it hard to balance sustainability with profitability.
Labor Shortages
Labor shortages present another critical challenge, especially in regions where manual harvesting is essential for producing high-quality coffee.
- Aging Workforce: In many coffee-growing regions, farmers are aging, and younger generations are less inclined to take up farming due to the physically demanding nature of the work and the uncertain financial returns.
- Migration to Urban Areas: As younger workers move to cities in search of better-paying jobs, the labor pool in rural farming communities is shrinking. This labor shortage increases the cost of harvesting, particularly for farms that rely on hand-picking methods.
In response to these challenges, the future of coffee farming lies in sustainability and innovation. Let’s see how farmers are embracing eco-friendly practices and technology to safeguard the industry.
The Future of Coffee Farming: Sustainability and Innovation
As the coffee industry continues to grow, sustainable practices and technological innovations will play a key role in adapting to environmental and economic challenges. By focusing on eco-friendly farming methods and leveraging new technology, coffee farming can continue to thrive despite these pressures.
Embracing Sustainable Practices
The future of coffee farming relies on adopting regenerative agriculture and agroforestry methods. These approaches focus on improving soil health, restoring ecosystems, and reducing carbon emissions. Techniques like drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting help conserve vital water resources.
Technological Innovation
Technology is transforming coffee farming by introducing more efficient and eco-friendly systems:
- Precision Agriculture: Farmers use sensors and drones to monitor crops, applying resources more precisely and reducing waste.
- Renewable Energy: Many farms are switching to solar power and biogas systems, cutting down on fossil fuel use and lowering carbon emissions.
As we look ahead, it’s clear that the future of coffee depends on a thoughtful combination of sustainable farming practices and cutting-edge innovations. Here’s how we can all contribute to shaping that future.

The Final Sip: Shaping the Future of Coffee
The future of coffee farming is at a critical turning point. The choices we make today will define how the industry adapts to sustainability challenges in the years ahead. By supporting sustainable practices and embracing innovation, we can ensure that coffee farming continues to thrive despite the pressures of climate change and economic instability.
Sustainability in coffee farming goes beyond protecting the environment. It’s about empowering farmers, preserving their livelihoods, and maintaining the rich traditions that coffee-growing communities have fostered for generations. In doing so, we guarantee that future generations can continue to enjoy the distinctive flavors that make coffee such a beloved global staple.
Your decisions as a coffee consumer play a significant role in shaping this future. Every time you choose sustainably sourced coffee, you contribute to a movement that supports the planet and uplifts the people behind your favorite brew. It’s a journey we all share, and together, we can make a lasting impact on the world of coffee.
I’d love to hear how you’re making a difference! Share your questions, thoughts, or experiences with sustainable coffee farming in the comments below. Let’s keep the conversation going and inspire each other to take action.

It’s amazing to see how sustainable farming practices can influence our consumption habits in all areas, especially coffee. We must encourage these practices because they show our care for the environment and the hardworking farmers who bring us our daily brew. Ensuring that these farmers receive their fair share is so important. Thank you for highlighting this crucial topic.
Thank you for sharing such thoughtful insights! It’s heartening to hear from readers who recognize the profound impact that sustainable farming can have on both our environment and the lives of the farmers who nurture each coffee plant.
I deeply believe that when we choose to support ethical practices, we’re contributing to a cycle of positive change—honoring the dedication of farmers and promoting a fairer distribution of resources. Your acknowledgment of this is truly encouraging.
I’m grateful that the post resonated with you. If there’s a particular aspect of sustainability or coffee culture you’d like to explore further, I’d love to hear your ideas!
Hi Sonia,
I have to admit I’m not a coffee drinker myself, but I found myself fascinated by your post on sustainable coffee farming practices. It all started when my wife and I visited the islands and saw a few coffee fields. The journey from seed to harvest is incredible, and I appreciate how you’ve highlighted the importance of sustainable methods.
Your insights into shade-grown coffee and its benefits for the ecosystem are eye-opening. It’s great to see how these practices enhance the quality of coffee and support local communities and biodiversity. Your exploration of the different coffee varieties and their specific needs really brought the topic to life!
Keep up the great work; I look forward to reading more about sustainable practices in the future. It’s wonderful to see such essential topics getting the attention they deserve!
Best wishes,
Opa
Your journey through the coffee fields sounds truly captivating! It’s fascinating how witnessing the origins of coffee can spark interest, even for those who don’t drink it. I’m delighted that my post connected with you in that way.
Sustainable coffee farming is a topic I’m deeply passionate about. It’s heartening to know that your insights into shade-grown coffee and its benefits resonated with you. Practices like these not only nurture the environment but also uplift local communities—a synergy that’s essential for our planet’s future.
Thank you for sharing your experience. Perhaps one day, a sustainably grown cup will pique your interest! Until then, feel free to share any thoughts or questions—you might just inspire my next article.